Key Takeaways
- MBTI functions are the cognitive functional preferences that determine how each one of the 16 personalities function in the real world.
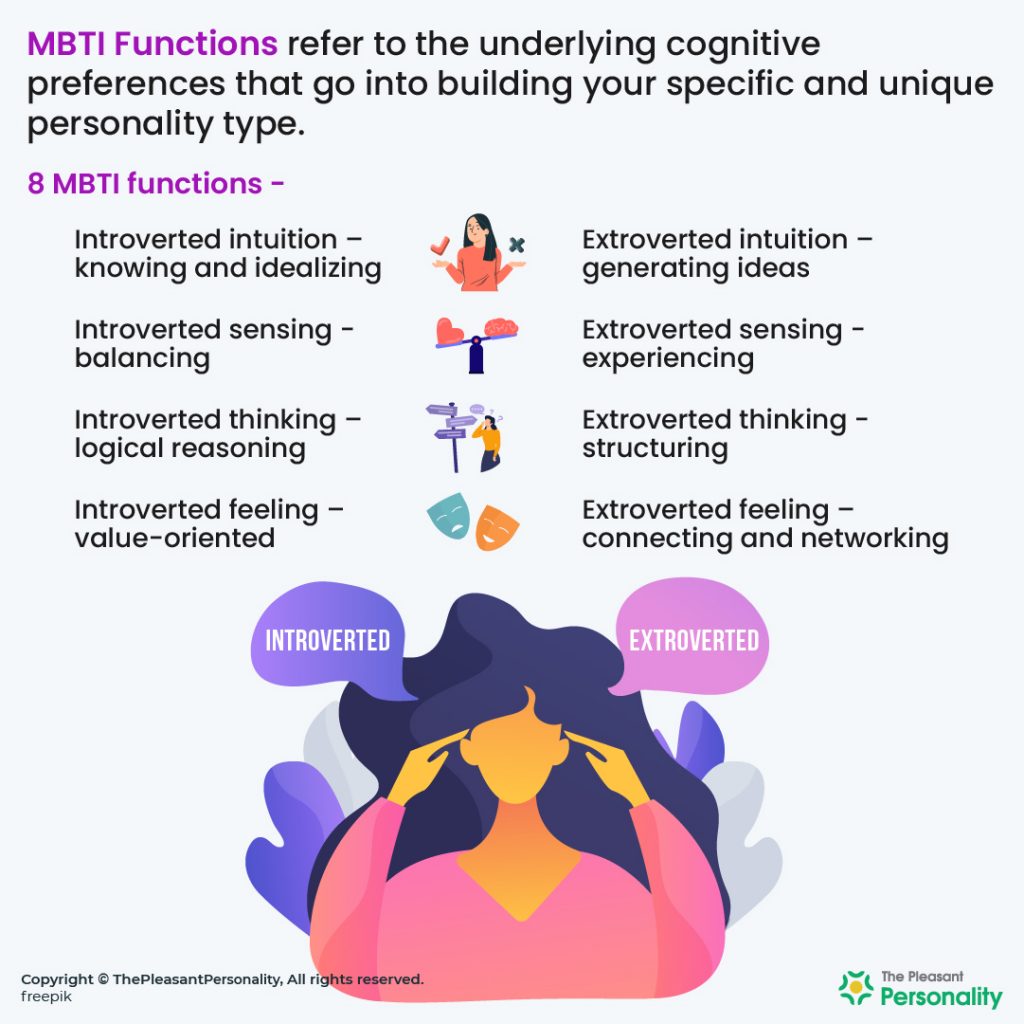
- There are eight cognitive functions – four of them operate in the introversion domain and the other four work in the extroversion domain.
- The four introverted functions are introverted sensing, introverted intuition, introverted thinking, and introverted feeling.
- The four extroverted functions are extroverted sensing, extroverted intuition, extroverted thinking, and extroverted feeling.
Many times you must have heard someone saying that they are an ISTJ or ENTP. These four-letter words sound confusing if you do not know what they mean. Right?
These are personality types described in the 16 personalities in the MBTI personality test. Each one of these types is based on some functional preferences known as MBTI functions.
The functional preferences describe the backdrop theory of how each personality type functions and comprehends the outer world. It also helps you to understand why you and someone else are different.
Are you interested to know why two people interacting with similar situations respond differently? What are the factors that make two people tick and live happily with each other?
This article will delve deeper into the various cognitive functions that help you to sense more about yourself and others in real-life situations.
Read on…..
MBTI Functions Infographic
MBTI Meaning
SUMMARY
MBTI refers to Myers Briggs Type Indicator, a personality test developed by the mother-daughter duo Katherine Briggs and Isabel Briggs Myers in 1944 and later revised in 1956.
MBTI is a self-report personality test, a psychological instrument that measures 16 types of personalities. This is a widely used test worldwide.
The theoretical background of MBTI and Myers-Briggs personality types dates back to Carl Jung’s personality theory which says that the subtle individual differences between people are based on some basic differences in their perception and decision-making process.
He referred to perception as an integral process of information processing where the person either uses his sensation preference or intuition function to be aware of people, things, and situations around them.
Jung referred to judgment as a way to reach decisive conclusions about what has been perceived and acknowledged about the physical reality.
In developing the MBTI, Katherine Briggs and Isabel Myers used Jung’s personality theory and the cognitive abilities therein.
If you differ significantly from the other person in the way you perceive information and reach a conclusion, it is evident that you will differ in your outlook towards life in general.
Even your attitude, communication style, values, and interests will also vary accordingly.
The four dichotomous cognitive functions that formed the basis of MBTI are –
TAKE OUR FREE PERSONALITY TESTS
Evaluate yourself with our personality tests that are clinically approved by Certified Psychiatrist and draw a path to successful work life and happy relationships.
Cognitive Function Definition
SUMMARY
Cognitive functions refer to the brain-based abilities and mental functions that help a person to think, feel, and act in various ways.
These functions typically contribute to learning and working memory, thinking and concept formation, reasoning, problem-solving, and decision making.
The cognitive functions also play a vital role in the perception and acquisition of knowledge. It helps the person understand whether their inner world and outer world are in sync with each other.
In the words of Carl Jung, cognitive functions refer to the various mental processes that help the individual to process information and conceptualize the world around them.
He referred to sensing vs intuition, thinking vs feeling, and judging vs perceiving as the principal ways to comprehend the world around you.
These cognitive functions actually form the premise of the MBTI personality inventory. Moreover, these cognitive preferences can be manifested either in an introverted function or in an extroverted manner.
A brief history of the MBTI assessment tool or the personality test
The inspiration to develop MBTI came to Katherine Briggs and her daughter Isabel Myers from the classic personality theory of Swiss psychiatrist Carl Jung.
Briggs started her research on understanding individual differences in 1917 when she met her would-be son-in-law who appeared somewhat different from her own family.
Thus, in order to know the underlying factors that determine human personality dynamics, Briggs continued her work and conceptualized four distinct temperament types.
These four types were
- Meditative or thoughtful
- Spontaneous or lively
- Executive
- Social
When Carl Jung’s personality theory became popular in 1923, Katherine Briggs found that her concept of temperaments matches with the Jungian concept of personality typing.
After an extensive study of Jung’s theory, Briggs came to the conclusion that individual differences in personality development arise from changes in perceptual and judging functions.
It means that if the information processing is different, the conclusion and the decision based on such perceptions ought to be different.
Later on, Briggs was joined by her daughter Isabel in 1919. Though both of them did not have any formal knowledge of the subject matter of psychology, they felt interested to know why human beings differ in their way of information processing, reviewing, and judging functions.
The work for the MBTI test development started during World War 11, with a motive that understanding personality types will help the women folks to get jobs in the industrial workforce across the wartime nations.
The Briggs Myers Type Indicator manual was first published in 1944. Years later, the handbook was updated and published again in 1956.
The MBTI manual earned support from the works of Henry Chauncey and some University professors such as Donald W. MacKinnon, head of the Institute of Personality and Social Research at the University of California, Berkeley; W. Harold Grant, a professor at Michigan State University.
After the demise of Isabel Myers in 1980, the second edition of the MBTI manual was revised and updated by Mary McCauley in 1985.
Again in 1998, the MBTI manual was again revised in a new way with an advanced level of the scoring system.
MBTI Cognitive Functions
In this section, we will discuss the cognitive functions and mind preferences that have gone into making the 16 personality types.
There are four cognitive functions out of which the first three were the brainchild of Carl Jung and the fourth function “Judging vs. perception” was introduced by Myers Briggs.
Jung proposed that the functions of sensing, intuition, thinking, and feeling will get manifested inwardly (introversion) or outwardly (extroversion).
These four functions are further divided into perceptual functions and judging functions.
The 8 subtype combination of functions is:
Perceiving function – in MBTI, sensing and intuition are the perceiving functions. It helps you to gather information from the external world and turn it into something concrete and meaningful.
It is very important to note that we all use the sensing vs. intuition function in our daily life.
However, the inclination to use a particular preference depends upon the attitudes you possess, the decision to be made, and the circumstances you are in.
Thus, the perceiving function can have either an introverted attitude or an extroverted attitude.
- Introverted sensing (Si)
- Extraverted sensing (Se)
- Introverted intuition (Ni)
- Extraverted intuition (Ne)
Judging functions – The judging functions play a role when you are required to make a decision in life.
- Introverted thinking (Ti)
- Extraverted thinking (Te)
- Introverted feeling (Fi)
- Extraverted feeling (Fe)
They are as follows:
1. Introverted sensing (Si)
People who prefer sensing and in particular, introverted sensors are focused inward. They have an inner subjective world that is rich and vibrant. These people are highly tuned towards internal bodily sensations.
At the same time, they are also aware of their external environment. They prefer to compare and contrast their present life with the past. Sometimes, they think too much about future opportunities and career planning as well.
Introverted sensors are also detail-oriented. They are quick to notice changes in their immediate environment.
Even if someone is showing changed behavior patterns, introverted sensors will be quite quick to notice the changes.
They are aware of bodily sensations such as hunger, thirst, pain, sex, etc. Sometimes, they may recall favorite moments of their life and can try to relate with some present happenings.
For example, they may look at a particular place and recall a particular event related to that place quite easily.
These individuals are quite nostalgic and prefer to remember and recall specific details that others might often ignore.
Introverted sensors are aware of the passage of time. They hold on to the moments through sensory images and patterns. They are fond of past traditions and beliefs.
At the same time, these people plan ahead for a bright and secure future.
Introverted sensing personality types are insightful and deep thinkers. They prefer routine and order and believe in trusted facts that have passed the test of time.
Some of the introverted sensing types are ISFJ, ISTJ, where Si acts as a dominant cognitive function. However, for ESFJ and ESTJ, introverted sensing is an auxiliary function.
Signs of introverted sensing
- Quick to notice inconsistencies in the physical reality
- Compares recent experiences with past events and tries to draw meanings and similarities out of it
- Learns quickly from mistakes and consciously avoids doing it again
- Introverted sensors are keen to know what can happen now or in future
- They prefer structure, routine, and consistency
- Introverted sensors can remember and recall significant people and events of their life vividly
- If something is out of place and not in tune with what it should be, introverted sensors can notice them easily
- They are systematic, cautious, and careful when it comes to accomplishing tasks
- Introverted sensing personalities prefer the clarity of thoughts and ideas. They like tried and tested methods and dislikes other ways of doing things
- They prefer to discuss ideas that can have a real-life application
- These people prefer humor but hardly show off their softer side to others.
2. Extraverted Sensing (Se)
Extraverted sensing refers to a cognitive function where a person uses his/her power of senses to gather information from the outer world.
It means that they receive only tangible and concrete information about what can be seen, heard, touched, or felt. If you are an extraverted sensor, you will always be detail-oriented.
Extraverted sensors focus on the present world that is literal and distinct. They are detail-oriented and prefer objective and concrete data. Any sort of ambiguity in perception is not for an extroverted sensor.
This cognitive preference derives its energy from the present moment. People who use this function are practical and realistic. They enjoy pure and unfiltered experiences.
Extroverted sensors prefer to relate with people, nature, events, and happenings going on around them.
It gives them sheer joy and enjoyment from directly interacting with their immediate physical reality.
This function typically looks into the present alone, never associating with events of the past or opportunities of the future.
Some of the extraverted sensing personalities are ESFP and ESTP. For them, this cognitive preference is a dominant function whereas, for the ISFP and ISTP, this is an auxiliary function.
Signs of extraverted sensing
- Highly in tune with the senses
- Objective, factual, and realistic
- Prefers to live in the tiny moments of life
- Down to earth, simple-minded, and practical people
- Focuses on detail, never misses out on anything that others may overlook easily
- Extraverted sensors are open-minded and flexible
- They are a lover of hands-on learning
- They are impulsive and go-getters.
- Extraverted sensors hate being tied down into commitments as they are free-willed and spontaneous
- Extraverted sensors hate being controlled. They don’t like others telling them how to lead their lives in general.
- loves to take risks and challenges because they are confident of surpassing all odds.
- They fully immerse themselves in the beauty and subtle details of life. They prefer to use their senses to absorb information from their immediate world.
3. Introverted intuition (Ni)
Introverted intuition is a cognitive function that focuses on the perception and information-gathering process where a person uses patterns and impressions, hidden meanings, to understand the future implications of the received information.
Isabel Briggs-Myers pointed out that introverted intuition gives you are the “flashes of inspiration, the insight into relationships, the imagination, the originality, the access to resources of the unconscious, the ingenuity, and the visions of what could be.”
This perceptual preference uses intuition and gut feeling to perceive information as true or valid. There is a sense of knowing what can happen in the future. Introverted intuition relies on inspiration and abstract concepts to know the truth.
People who use this cognitive function prefer intuition over the sensing function. They are independent and future-focused.
They do not like to live in the present moment, whereas they try to formulate their future path based on their present skills and know-how.
Dominant introverted intuitiveness is focused elsewhere. They never live in the moment they are rather they navigate their mind to some other situation, probably in the future.
These people are keen to see the big picture, often ignoring the details of an event. They are the trailblazers of the future. They love theories and complex concepts and avoid small talk and mundane activities.
The personality types that predominantly use introverted intuition are INTJ and INFJ.
The ENFJ and ENTJ also use introverted intuition as a secondary cognitive function, just to support their thinking vs. feeling functions.
Signs of introverted intuition
- They are insightful and driven by inspiration and abstract ideas.
- Introverted intuitive prefer strategies and methods
- Obscure ideas and abstract thoughts interest them a lot.
- They prefer to know the underlying meanings of everything
- Their perceptual processes are hard to be explained in words
- Prefers alone time to ponder and daydream
- Likes to see the big picture rather than focusing on the details
- They prefer to know the ‘why’ and ‘how’ of everything
4. Extroverted Intuition (Ne)
People with extraverted intuition function prefer to view the world in terms of theories and complex knowledge. For them, meaning is derived from abstract connections between ideas as perceived from the outside world.
Extroverted intuition focuses on the objective and realistic world to find connections and relationships between people, events, things, and objects they sense around them.
These individuals try to discover a brand new meaning out of the perceived information. They seek thrill, changes, and challenges in life that may help them to perceive new information every now and then.
The two dominant users of extraverted intuition are ENFP and ENTP. However, INFP and INTP use extraverted intuition as an auxiliary function.
These people follow their gut feeling in analyzing the situations and derive meanings out of it. They are good at understanding the hidden meaning and make varied interpretations of the physical world.
They can see future possibilities and can juggle ideas and concepts that may bring future success.
Extroverted intuition means their instinctual tendencies are directed outwardly. They enjoy deeper conversations with others, brainstorming, and imaginative play.
People who use extroverted intuition as a dominant function are very goal-oriented and productive.
They have the ability to think and explore various hobbies and interests. They are good at integrating various ideas and fitting them in a definite frame.
Signs of extroverted intuition
- Extroverted intuition is driven by new possibilities
- They like tough tasks and challenges
- Routine and mundane jobs can be frustrating and they prefer change and innovation
- People who are high in extroverted intuition function are future-focused. Sometimes that may lose track of what’s happening in the present moment
- They are good at finding connections between events and circumstances
- Innovative ideas and generating a good amount of information from a brainstorming session motivate them.
- Extroverted intuitive tries to find a novel solution to a problem. They hardly use time-tested methods because they see them as outdated and not trustworthy.
- They are focused more on abstract theories and possibilities. Eager to know what can happen or can be done rather than what is still in place
- Uninteresting stuff and conversations are boring and nerve-racking
- They are open-minded, flexible, and adaptable to changed circumstances
Now let us study the details of the judging functions in personality typing.
5. Introverted thinking (Ti)
Introverted thinkers are turned toward an inner world. They prefer to gain clarity and a vivid understanding of the real world by using their strong powers of instincts and intuition.
If you are an introverted thinker, you will form an internal framework about how things operate. You are logical, filled with reason and deep understanding.
There will be a strong preference to develop a power bank of knowledge that is modified by various life experiences from time to time.
People who use introverted thinking as their primary mode of functioning are usually quiet and reserved.
They prefer to operate at a deeper level and avoid being messy and unsystematic in their way of thinking and feeling.
Introverted thinking is a decision-making function where the Person uses their gut instincts to understand the ‘why’ and ‘how’ of things happening around them.
It is an impersonal and objective understanding that looks at the big picture before making a decisive decision. These people never get swayed by emotions and try to remain impartial and rational as much as possible.
They use common sense as a means to delve deeper into the details of a subject matter.
Being an inside person, Ti may question and analyze every small piece of information that comes to them. Thus, they tend to put the disjointed parts in a complete whole.
Introverted thinkers prefer to work alone, defy conventions, and are ready to make out-of-the-box decisions. These people are fair and just.
They are not biased and prefer to stay aloof from emotional decisions based on mood swings or other affective responses fully.
Signs of introverted thinking
- Impersonal and fiercely objective in their thought processes
- They never think aloud but prefer to be quiet with their decision-making process. You are not the one to go and tell people what you actually did. Right?
- Introverted thinkers may decide slowly because they prefer being slow and put a lot of time into thinking about what needs to be done next in line.
- They never accept facts at face value, rather prefer to decide whether the facts are in tune with their objective frame of mind.
- Introverted thinkers are logical, honest, and rational
- They dislike generalized statements. Prefers to fit in the right words at the right place.
- They never hurry up to decide on anything. There is a tendency to think and ponder in detail to arrive at a concrete decision.
- Their minds are organized where complex information is broken down into parts to think in a piecemeal method. They like to organize facts and have an inner world of truths and conviction that belongs only to them.
- They love to debate and argue over known and unknown topics
- Since thought processes are internalized, introverted thinkers may struggle to verbalize their point of view to others.
- They are fiercely autonomous and independent. Always prefer to figure out their own ways of doing things.
6. Extraverted Thinking (Te)
Extraverted thinking is a cognitive function that helps to make concrete decisions. This function helps the person to separate emotions from logic and reasoning.
Facts and details of events are organized and structured to keep them aside from subjective feelings. Extroverted thinkers are fair, just, and logical-minded.
They use cause-effect relationships before deciding on anything.
The Te users prefer to understand the detailed pros and cons of a situation to arrive at a proper decision. They never decide on haste.
Extraverted thinking is projected outside. It means people who use this function prefer to organize and evaluate data that they have received before making a decision.
They are efficient and can inspire others to do things the way they want. Being an extrovert type, these people are social, active, and can organize people and systems to work together.
Extroverted thinkers like clarity and they are not influenced by emotions and feelings. In most situations, they prefer to keep things straightforward and precise.
These individuals showcase a liking for arguments and discussions. They are good at implementing new ideas and can inspire others to follow what they say.
The personality types who use extraverted thinking are the ENTJs and ESTJs. However, for the ISTJs and INTJs, extraverted thinking acts as a secondary cognitive function.
Signs of extraverted thinking
- You have the power to influence people and get the job done
- Remains unmoved by tears and smiles. It means they keep feelings at bay when it comes to decision-making.
- Extroverted thinkers prefer to follow a schedule and are not at all messy in the way they accomplish tasks
- They prefer to do things on time, never procrastinate
- They prefer to have rules and procedures lined up whenever needed.
- Extraverted thinkers prefer to think out loud and are highly organized
- Being prepared to face the extreme is your trump card
- They enjoy planning but are quick decision-makers. Puts things to the conclusion pretty early
- Being a competent person, extroverted thinkers are never lazy. They will do what they are supposed to do with precision and perfection
7. Introverted feeling (Fi)
They are value-oriented and put emphasis on emotions and feelings while making important decisions in their life.
This is a judging function that involves a person’s deep awareness of values and moral integrity. Introverted feelers prefer peace and harmony.
Their life is driven by values and those are actually private and intimate. They will hardly express their deepest desires, feelings, and values publicly.
People who are high in this cognitive function are fiercely honest in the way they live their life. They maintain authentic social connections and are quite compassionate about others.
Introverted feelers are introspective. They tend to look within to connect the past experiences with the new ones. They can also understand the hidden feelings of others.
As you are honest and practical-headed, you do not like phony behavior. You will avoid social niceties and will prefer to remain authentic as far as possible.
They also value freedom of expression. During unhealthy states, introverted feelers may appear self-centered and superior. They may restrict their path of growth by being socially unpopular and arrogant.
People who use this cognitive function as a dominant pattern will exhibit unrealistic expectations from the ‘self’ and others.
They are idealists who are artistic and live with ethics and moral judgments. Fi happens to be a dominant function for the INFPs and ISFPs.
However, for the ENFP and ESFP, the introverted feeling is a way towards growth and cats as an auxiliary function.
Signs of introverted feeling
- They are sincere and upfront.
- This function makes a person dislike small talk
- Your hunch never goes wrong when things are out of place, though you’re not always sure where do these feelings come from
- You are private when it comes to sharing your deepest feelings with someone
- Introverted feelers have their unique style and taste. They are not much bothered about what others may think or feel about their preferences and lifestyle
- You will never force others to believe or conform to your set of values
- Being an introverted feeler also means you are tolerant, easygoing, and strongly rooted in your values and conscience
- As your emotions are hidden and private, you appear enigmatic in front of others. People feel confused when they are with you, probably because you are not an open book to be read and shared by all
- You hate to critically evaluate others and also hate being criticized
- You prefer to explore and experiment and would hate being stuck
- Introverted feelers are empathetic. They are quick to understand the feelings of others
8. Extroverted feeling (Fe)
The extroverted feeling is empathetic and kind. People who are the users of this cognitive function are well aware of social dynamics. They are the helpers for the poor and the downtrodden.
These people love to share and are emotionally expressive and clear. They dislike ambiguous decision-making and thus follow a straight-cut way of dealing with things.
Extroverted feelers have a good communication style. They are diplomatic and understanding. Most often, you may see them helping others meet their goals.
Extroverted feelers prefer deeper social and emotional connections. They are friendly, sociable, and open-minded. Sometimes they are polite and generous as well.
Extroverted feelers are good at understanding the moods of others in a specific situation.
Signs of extroverted feeling
- They are aware of the expectations of others from them
- Peace and harmony reside with an extroverted feeler. They are the mediators and peacemakers
- Extroverted feelers are kind and generous
- Busy to meet the needs of other people nada my forget about oneself
- They like to discuss their decisions with other like-minded people so as to know whether the decisions can affect people’s life positively
- They are driven by values and places emphasis on right and wrong stuff
- Extroverted feelers may feel responsible for how others are feeling in a situation. They are quick to notice changes in mood, facial expressions, and tonal quality
MBTI Functional Stack
The Myers and Briggs theory of psychological types and the setting up of the Myers Briggs foundation happens to be hallmark research in personality types to date.
The MBTI functional stack refers to the ordering of the various functions that we have discussed so far.
It means the hierarchical organization of the eight functions in the 16 personality types discussed in the personality inventory.
Each type is made up of four functions from which the four-letter type has been constructed. For example, INTJ means introverted, intuitive, thinking, and judging personality type.
In the functional stack, the ordering of the functions is ranked according to their degree of influence or strength on that type.
It also symbolizes the extent to which the function makes its conscious appearance in a person’s personality profile.
Thus, the cognitive functions are stacked as dominant function, auxiliary function, tertiary function, and inferior function.
- Dominant function – It refers to the major functional preferences that tend to dominate and influence the most in building up your personality type. This function is well developed and has more power and influence than the other functions.
- Auxiliary function – The auxiliary function refers to the secondary preferences that are not so well developed, yet influence the person’s innate nature to a considerable extent. It plays a supporting role in the dominant functions.
- Tertiary function – These functions are not so well developed and are contradictory to the auxiliary function. For example: If your auxiliary function is sensing, your tertiary function will be intuition.
The tertiary function develops later in life when you will realize the importance of looking at other perspectives in life.
This function helps you to develop your weak areas, maybe the parts of yourself that you have ignored and avoided for a long time.
- Inferior function – The inferior function operates at the unconscious level. When stress dominates your psyche, you may seem to disintegrate and behave in certain ways that are not usual for you.
This function operates when the resources are depleted and you may need to cope with the stress in some way or the other.
Perhaps this function may make you an immature, less controlled type. You may feel hopeless and out of place.
The chart shown below describes the functional stacking of all the 16 personality types for your quick understanding of the MBTI functions.
Your four-letter MBTI type symbolizes the four functions in the form of a functional stack. For example, an INTJs functional stack will look like this – Ni, Te, Fi, Se
For an INTJ, introverted intuition is the dominant function; extroverted thinking is the auxiliary function; introverted feeling is a tertiary function, and extroverted sensing is their inferior function.
| Personality type | Dominant functions | Auxiliary functions | Tertiary functions | Inferior functions |
| INTJ | Introverted intuition (Ni) | Extraverted thinking (Te) | Introverted feeling (Fi) | Extraverted sensing (Se) |
| INTP | Introverted thinking (Ti) | Extraverted intuition (Ne) | Introverted sensing (Si) | Extraverted feeling (Fe) |
| ENTJ | Extraverted thinking (Te) | Introverted intuition (Ni) | Extraverted sensing (Se) | Introverted feeling (Fi) |
| ENTP | Extraverted intuition (Ne) | Introverted thinking (Ti) | Extraverted feeling (Fe) | Introverted sensing (Si) |
| INFJ | Introverted intuition (Ni) | Extraverted feeling (Fe) | Introverted thinking (Ti) | Extraverted sensing (Se) |
| INFP | Introverted feeling (Fi) | Extraverted intuition (Ne) | Introverted sensing (Si) | Extraverted thinking (Te) |
| ENFJ | Extraverted feeling (Fe) | Introverted intuition (Ni) | Extraverted sensing (Se) | Introverted thinking (Ti) |
| ENFP | Extraverted intuition (Ne) | Introverted feeling (Fi) | Extraverted thinking (Te) | Introverted sensing (Si) |
| ISTJ | Introverted sensing (Si) | Extraverted thinking (Te) | Introverted feeling (Fi) | Extraverted intuition (Ne) |
| ISFJ | Introverted sensing (Si) | Extraverted feeling (Fe) | Introverted thinking (Ti) | Extraverted intuition (Ne) |
| ESTJ | Extraverted thinking (Te) | Introverted sensing (Si) | Extraverted intuition (Ne) | Introverted feeling (Fi) |
| ESFJ | Extroverted feeling (Fe) | Introverted sensing (Si) | Extraverted intuition (Ne) | Introverted thinking (Ti) |
| ISTP | Introverted thinking (Ti) | Extraverted sensing (Se) | Introverted intuition (Ni) | Extraverted feeling (Fe) |
| ISFP | Introverted feeling (Fi) | Extraverted sensing (Se) | Introverted intuition (Ni) | Extraverted thinking (Te) |
| ESTP | Extraverted sensing (Se) | Introverted thinking (Ti) | Extraverted feeling (Fe) | Introverted intuition (Ni) |
| ESFP | Extraverted sensing (Se) | Introverted feeling (Fi) | Extraverted thinking (Te) | Introverted intuition (Ni) |
MBTI Personality Types
There are 16 personality types described in the MBTI personality test. Each type has its own unique signs that are unmatched.
However, each one of these 16 types shares eight cognitive functions as already discussed in the previous section of the article.
The MBTI personality types are–
How to develop cognitive functions?
Your cognitive fitness shows your overall psychological health and well-being. If you engage in a variety of daily habits and mental exercises, it will surely improve cognitive functioning.
The mental faculties such as memory, thinking, reasoning, and problem-solving capabilities will improve to a great extent.
Some of the best ways to improve cognitive functions could be –
- Regular physical exercise improves neural connections and improves brainpower.
- Getting exposed to varied experiences in life. It helps to improve one’s problem-solving skills.
- A curious drive to know, explore, and experiment with various things develops your perceptual processes.
- Social connections also help to improve cognitive functioning. A lot of smiles and cheers around you can actually motivate you to improve your learning habits and memory functioning.
- Living in the moments of life helps to improve your sensing and intuition functions.
- Practice meditation to improve levels of attention and concentration. Henceforth, it also improves long-term memory and problem-solving abilities.
- Brain training games, solving various kinds of puzzles help in developing your mental faculties. It improves creativity, problem-solving skills as well.
- You should have enough sleep to keep stress at bay. It also helps in memory consolidation and improves memory functioning.
Parting words from ‘ThePleasantPersonality’
To conclude, it’s important to note that knowing MBTI functions can actually help you to understand the underlying psychological processes that go into making ‘who you are
When you know your mind’s inclination towards a specific cognitive function, you will be in a better position to understand the perceiving and judging functions.
When you know your personality type and the underlying functions, it helps you to improve those skills that are weak. It also adds value to the strong areas that you possess.
Perhaps, functional analysis can guide you to understand your feelings and actions and why you behave the way you do.
Sometimes, it is vital to know your strengths and weaknesses of yourself so that you can take timely action to become your best ‘self’.
We get little commissions for purchases made through links in this post. Our editors carefully choose to promote only those products/services that resonate with our readers.




